Every thing you need to understand before Starting Limited Liability Partnership
Starting a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a great option for businesses looking for flexibility and protection. An LLP allows partners to manage the business freely while limiting their personal responsibility for debts. It’s a good choice for start-ups, small businesses, and professional firms. To set up an LLP, you need to pick a unique name, get digital signatures for all partners, and submit the required documents to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA). You’ll also need to create an agreement outlining each partner’s roles and responsibilities. After registration, LLPs must file yearly forms and keep proper financial records. With its simple structure and legal benefits, an LLP is a smart way to grow your business safely.

What is an LLP ? and Key Features Explained
A Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a type of business structure that combines the features of a partnership and a company. In other words, it allows two or more people to run a business together while limiting their personal financial risk. Specifically, in an LLP, the partners are only responsible for the amount of money they have agreed to invest, and their personal assets are protected from business debts. Moreover, an LLP is treated as a separate legal entity, meaning it can own property, sign contracts, and continue to operate even if one partner leaves. Additionally, with no minimum investment required and fewer rules to follow compared to a company, LLPs are a popular choice for small businesses, start-ups, and professionals who want a simple and safe way to start and grow their business.
key Features
Limited Liability Protection
Partners’ personal assets are protected, and they are only liable up to their investment in the business.Separate Legal Entity
The LLP is an independent legal entity, allowing it to own property, enter contracts, and continue operations even if a partner leaves.No Minimum Capital Requirement
LLPs can start with any amount of capital, making it accessible for small businesses and startups.Operational Flexibility
Partners have the freedom to manage the business directly without a rigid corporate structure.Tax Advantages
LLPs are not subject to Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT) and enjoy lower compliance costs.Perpetual Succession
The business remains unaffected by changes in partnership, ensuring continuity.Simpler Compliance Requirements
LLPs have fewer filing and regulatory obligations compared to private companies.Global Recognition
LLPs are widely accepted internationally, making it easier for businesses to expand and attract investments.Profit-Sharing Flexibility
Partners can decide their profit-sharing ratios, irrespective of their capital contribution.Suitable for All Types of Ventures
LLPs are ideal for start-ups, small businesses, and professional service providers looking for a cost-effective and secure business structure.
Rules and Regulations for Limited Liability Partnerships (LLP)
Incorporation and Registration:
- Register with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
- Submit necessary documents and the LLP Agreement within 30 days of incorporation.
LLP Agreement:
- Draft and file an LLP Agreement detailing partners’ rights, duties, and operational guidelines.
Designated Partners:
- Minimum of two designated partners, with at least one being an Indian resident.
- Designated partners are responsible for statutory compliance.
Compliance Requirements:
- File Annual Return (Form 11) within 60 days of the financial year-end.
- Submit Statement of Account and Solvency (Form 8) annually.
Tax Filing:
- File annual Income Tax Returns for the LLP.
Audit Requirements:
- Mandatory for LLPs with a turnover above ₹40 lakhs or contribution exceeding ₹25 lakhs.
Maintenance of Books of Accounts:
- Maintain accurate financial records on a cash or accrual basis.
Perpetual Succession:
- LLP continues irrespective of changes in partnership.
No Minimum Capital Requirement:
- LLPs have no mandatory minimum capital investment.
Penalties for Non-Compliance:
- Fines of ₹100/day for late filings, with no upper limit. Continuous default may result in legal action.
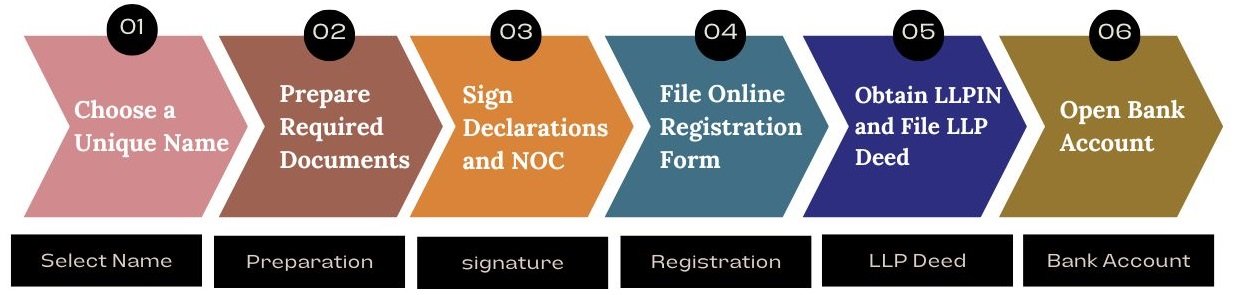
How to Register an LLP in india ?
Choose a Unique Name
Select a distinct name ending with “LLP” and ensure it meets legal requirements.Prepare Required Documents
Gather and organize all necessary documents for registration.Sign Declarations and NOC
Complete the Declaration and No Objection Certificate (NOC) via remote or digital signing.File Online Registration Form
Submit the incorporation application through the MCA portal.Obtain LLPIN and File LLP Deed
Receive the Certificate of Incorporation (LLPIN), draft the LLP Agreement, and file Form 3.Open Bank Account
Set up a business bank account and commence operations.
Document Required for LLP Registration in India
Following Documents required for LLP Registration Process
- PAN Card of Partners
- Aadhar Card of Partners
- Bank Statement of Partners
- Photo of Partners
- Mobile and Email id
- LLP Address – Electricity Bill (Latest) (With Owner NOC)
Understanding LLP Formation Costs
LLP Registration Package @ ₹8,000
Get Easy LLP registration with our all-inclusive package:
- LLP Registration
- Government Fees & Stamping
- Notarized LLP Deed
- DIN & DSC for 2 Partners
- PAN & TAN Registration
- Form 3 Filing
- MSME, PF & ESIC Registration (if required)
Your nearest LLP consultant for a smooth and compliant registration process!
Essential Records to Maintain for an LLP in India
Maintaining accurate accounting records is crucial for LLPs to ensure compliance and financial transparency. Here’s a concise list of key records that every LLP must maintain:
- Books of Accounts: Detailed records of income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and partner contributions, maintained on a cash or accrual basis.
- Invoices and Receipts: All sales, purchase, and expense records, including supporting documents like bills and vouchers.
- Bank Statements: Regularly updated and reconciled records of all bank transactions.
- Profit and Loss Statement: Summarizes income and expenses to assess profitability.
- Balance Sheet: Reflects the LLP’s financial position, including assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Tax Records: Includes GST filings, income tax returns, and TDS documentation, if applicable.
- Partner Contributions: Records of each partner’s capital contributions and any changes.
Retention Period: Records must be preserved for 8 years at the LLP’s registered office or an approved location.
Maintaining these records ensures legal compliance, simplifies audits, supports decision-making, and fosters sustainable business growth. Proper accounting is the backbone of every successful LLP!
Audit of LLP in India
The audit of a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a crucial process to ensure financial transparency and compliance with legal requirements. Under the LLP Act, 2008, an audit is mandatory if the LLP’s annual turnover exceeds ₹40 lakh or if the capital contribution is more than ₹25 lakh. Additionally, a tax audit may be required under the Income Tax Act if the turnover exceeds ₹1 crore in business or ₹50 lakh in professional services. The audit process involves appointing a Chartered Accountant (CA), preparing financial statements such as the balance sheet and profit & loss account, and having them verified for accuracy and compliance. An audit provides numerous benefits, including enhanced financial transparency, better decision-making, and compliance with statutory requirements, thus avoiding hefty penalties. Even when an audit is not mandatory, LLPs are encouraged to maintain proper records and voluntarily conduct audits to build trust and credibility with stakeholders.
Why LLP is Better than Partnership Firm?
A Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) and a partnership firm are two types of business structures through which partners can carry out their business. A minimum of two persons willing to be partners are required to establish an LLP or a partnership firm. LLP is a new concept, while a partnership firm is an old concept. The concept of LLP was introduced in 2008 through the Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Act. However, partnerships in India have been established under the Indian Partnership Act since 1932. Though an LLP and partnership firm requires a partnership between two parties for its establishment, it has many differences.
LLP (Limited Liabilities Partnership)
- Best of Both Worlds: Combines partnership simplicity with company-level legal protection.
- Limited Liability: Partners are liable only up to their contributions—no personal risks.
- Clear Accountability: Each partner is responsible for their actions.
- Ideal for Professionals: Perfect for startups, SMEs, and service-based businesses.
- Flexible & Growth-Friendly: Operational freedom that attracts investors.
LLPs: Secure, flexible, and built for success!
Partnership Firm
- Collaborative Model: Brings like-minded individuals together to pool resources, capital, and vision.
- Unified Entity: Partners share profits, responsibilities, and accountability equally.
- Easy Setup:
- Draft a partnership deed outlining roles and rules.
- Choose a name that reflects the firm’s identity.
- Flexibility: Registration is optional; the law recognizes unregistered firms.
- Shared Accountability: Partners are collectively responsible for the firm’s dealings and liabilities.
- Mutual Growth: A commitment to collaboration and achieving collective dreams.
Ideal for entrepreneurs seeking simplicity and shared success!